Can I Do More Business if I Accept Bitcoin?
A Basic Guide on How to Make Bitcoin Work for You
Bitcoin has become well-known around the world since first appearing in 2009. With so much publicity surrounding the technology, both positive and negative, many merchants are cautiously asking whether they should accept bitcoin as well.
This overview runs through the basics of what all online merchants need to know about bitcoin—including its potential risks and rewards, and how to safely incorporate bitcoin into your business.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a “cryptocurrency”—a digital currency traded through a decentralized, peer-to-peer network.
The value of an individual bitcoin in relation to hard currency—like the US Dollar—is based directly on a supply-and-demand principle. There is a finite number of bitcoins in the world, and their value is determined by how much of another currency a buyer is willing to trade.
Cryptocurrencies enable online transactions between two parties using blockchain technology, a kind of open spreadsheet that functions as a collective ledger. Each individual transaction is recorded in the blockchain, providing an ever-expanding and publicly-accountable record that still maintains the anonymity of the parties involved.
Though bitcoin first gained prominence for its association with illicit “dark web” sales in the early 2010s, people buy the currency for other purposes as well, such as online speculation. Bitcoin reached an all-time high of more than $2,000 in May 2017—over four times more than a year earlier. However, that value has fluctuated dramatically in short periods of time before, and it certainly will again.
Can Merchants Benefit from Bitcoin?
As an eCommerce merchant, there are quite a few potential benefits to accepting bitcoins:
Open to New Consumers
Bitcoin knows no borders. This enables businesses to work with international customers without the need to worry about handling different currencies or dynamic currency conversion (DCC). Plus, accepting bitcoin can give merchants a more “forward-thinking” image that appeals to younger consumers, particularly as the currency gains popularity.
Lower Fees
Conducting a bitcoin transaction involves fewer intermediaries than a traditional card transaction, resulting in lower costs per sale. While fees vary depending on the method used to exchange the bitcoins, they still tend to be much lower than traditional processors as a percentage of the total transaction.
No Risk of Chargebacks
Because of the way blockchain technology operates, all bitcoin transactions are final, completely non-reversible. This is in stark contrast to traditional payments, which are liable to the chargeback process, per the US Fair Credit Billing Act of 1974.
By dealing in bitcoins, customers assume responsibility for potential fraud and waive the ability to reverse charges. This makes friendly fraud impossible with bitcoin—a major incentive, given the $40 billion lost annually to chargebacks and chargeback-related expenses.
Is There a Downside to Accepting Bitcoin?
There are clearly benefits for merchants willing to accept bitcoin. However, the practice is not without drawbacks:
Volatility
The need to convert bitcoins into hard currency could translate to thousands of dollars in losses if the market suddenly bottoms out—as it has on multiple occasions.
The exchange rate for bitcoin is extremely volatile due to speculation. That volatility forces merchants to choose between offloading bitcoins as quickly as possible, or to keep them in reserve and engage in speculation themselves.
Potential Theft by Hackers
Bitcoins only exist as pieces of code, and as such, they are vulnerable to theft by hackers. This is the downside of the bitcoin transaction’s irreversible nature; once those funds are gone, there is no way to recover them.
When hackers stole $70 million worth of bitcoins from Bitfinex customers in 2016, the only way to compensate victims was by offering equity in the exchange’s parent company.
Taxes and Record-Keeping are Complicated
Businesses are still required to record and pay applicable taxes on bitcoin transactions. The IRS classifies bitcoins as property, meaning that the taxes owed on a bitcoin transaction will depend on both the exchange rate at the time the bitcoin was received, and the value at the time the bitcoin is cashed out. This can be a logistical nightmare for merchants attempting to trade bitcoins without an intermediary.
Should I Find a BMSP?
Whether the pros outweigh the cons is a matter of perspective, but more and more merchants are willing to take the bitcoin gamble. The easiest and safest way to accept bitcoins is through a bitcoin merchant service provider, or BMSP.
These services enable merchants to accept bitcoin and instantly transfer them into hard currency:
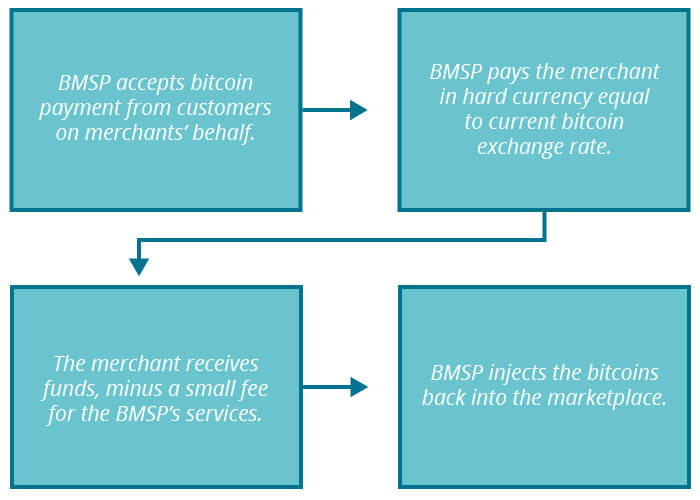
Merchants can enjoy the benefits of dealing in bitcoin without accepting many of the associated risks and responsibilities. By signing up with a service, most merchants can simply add a button to their site to allow checkout with bitcoin and be up-and-running almost immediately.
Choosing the right BMSP can be tricky. Before settling on a provider, merchants should ask the following questions to ensure that they’re not taken advantage of by bitcoin scams posing as legitimate BMSPs:
- Is the BMSP a registered MSB? Confirm that the candidate is a registered money services business, is fully compliant with all FinCEN regulations, and has an anti-money laundering compliance program.
- Is the BMSP a licensed money transmitter? Most legitimate BMSPs will be classed as a money transmitter in some states. Find out if the company is licensed in their own state, and if not, why.
- Will they pledge collateral? A licensed money transmitter is required to ensure their obligations to clients. This protects against fly-by-night scammers who may disappear with merchants’ funds.
- How does the BMSP decide exchange rates? Unlike national currencies, there is no single exchange rate for bitcoin. It is up to those involved in a transaction—the merchant and BMSP—to determine fair pricing for both parties.
- How do they handle refunds? Some BMSPs allow refunds in bitcoin, but not all. Merchants must ask about a BMSP’s policies regarding refunding customers, and how those policies are communicated to customers.
- Do they have access to customer information? Merchants should be sure to know the answer to that question and these as well: What are the BMSP’s policies regarding customers’ personal information? How do they collect and disclose data collected from their clients’ shoppers?
Take a Balanced Approach
Trading in bitcoin remains a niche preference, but interest in the technology is still growing fast. Merchants can position themselves for success by getting on-board with bitcoin early, but only if they guard against scams. For your protection—and the protection of your customers—choosing the right BMSP is crucial.
